"There's nothing worse than waiting for a build to complete, or those e2e tests to run. With Nx Cloud, our development team has saved over 104 hours, almost cutting our build times in half. The installation is seamless and the results are immediate. It's nice to have a tool that passively saves so much development time." - Director of Software Development, enterprise digital marketing firm
One of the most impactful core features of Nx is the affected graph. The affected graph helps us to skip unnecessary work and focus only on the things that have been changed, speeding up our CI and helping us ship features and hotfixes faster.
However, long-running tasks, especially End-to-End (E2E) tests, can become a significant bottleneck and prevent getting the code changes out faster. This is particularly true for monolithic projects, but also in cases when there is a single large E2E project that covers the entire scope of the application. In these scenarios, the full benefits of an affected graph cannot be realized.
In this guide, we'll explore three techniques to speed up your CI by splitting these lengthy test tasks.
Built-in Test Sharding
One of the simplest ways to split long-running tests is by using built-in test sharding features available in popular testing frameworks like Jest and Playwright. These tools allow you to divide your test suite into multiple shards that can be executed in parallel, reducing the perceived test execution time.
In Jest we can utilize the new --shard option to split your test suite. The example below shows splitting into 4 shards.
❯
nx affected -t test -- --shard=1/4
❯
nx affected -t test -- --shard=2/4
❯
nx affected -t test -- --shard=3/4
❯
nx affected -t test -- --shard=4/4
Playwright also supports the --shard option:
❯
nx affected -t e2e -- --shard=1/4
❯
nx affected -t e2e -- --shard=2/4
❯
nx affected -t e2e -- --shard=3/4
❯
nx affected -t e2e -- --shard=4/4
Now that we have our tests sharded, we can distribute the test load and achieve faster feedback. But what about the test runners that don't support sharding?
Nx Atomizer
For more granular control over test distribution, Nx offers the Atomizer. This feature allows you to split tasks per file. This splitting further allows us to distribute long-running tasks across a larger number of agents, providing detailed insights into flaky tests and enabling automatic re-runs. If one of the flaky tests fails, we will still cache the results of all the other task slices and can even have a successful run if the flaky test re-run succeeded.
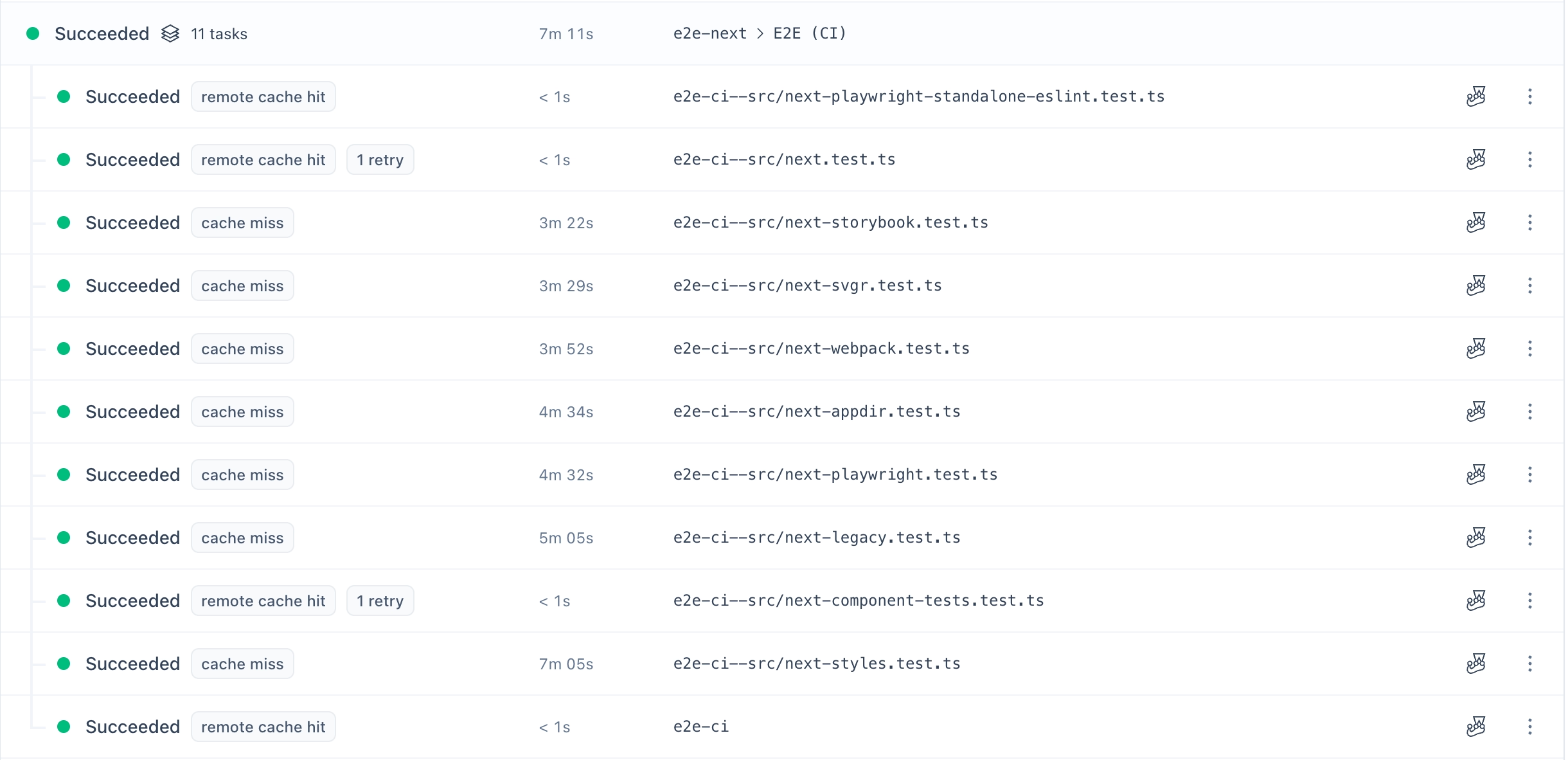
With Atomizer, you can achieve a higher level of parallelism and ensure that only the necessary tests are executed, further optimizing your CI pipeline.
To enable the Atomizer, we need to use supported inferred plugins or create our own.
1{
2 // ...
3 "plugins": [
4 {
5 "plugin": "@nx/cypress/plugin",
6 "options": {
7 "targetName": "e2e",
8 "ciTargetName": "e2e-ci"
9 }
10 },
11 {
12 "plugin": "@nx/playwright/plugin",
13 "options": {
14 "targetName": "e2e",
15 "ciTargetName": "e2e-ci"
16 }
17 },
18 {
19 "plugin": "@nx/jest/plugin",
20 "options": {
21 "targetName": "test",
22 "ciTargetName": "test-ci"
23 }
24 },
25 {
26 "plugin": "@nx/gradle",
27 "options": {
28 "classesTargetName": "classes",
29 "buildTargetName": "build",
30 "testTargetName": "test",
31 "ciTargetName": "test-ci"
32 }
33 }
34 ]
35}
36The test-ci and e2e-ci targets will automatically be split into the following format:
e2e-ci--path/to/test/filetest-ci--path/to/test/file
Or more generically:
{ciTargetName}--{path/to/test/file}
You can find more information on how to configure the Atomizer on the respective Jest, Cypress, Playwright, Gradle or follow this recipe to create your own inferred plugin.
Manual E2E Project Splitting
In addition to automated splitting like sharding or atomization, manually splitting E2E projects into scopes can provide additional significant performance benefits.
Let's look at the simplified graph below:
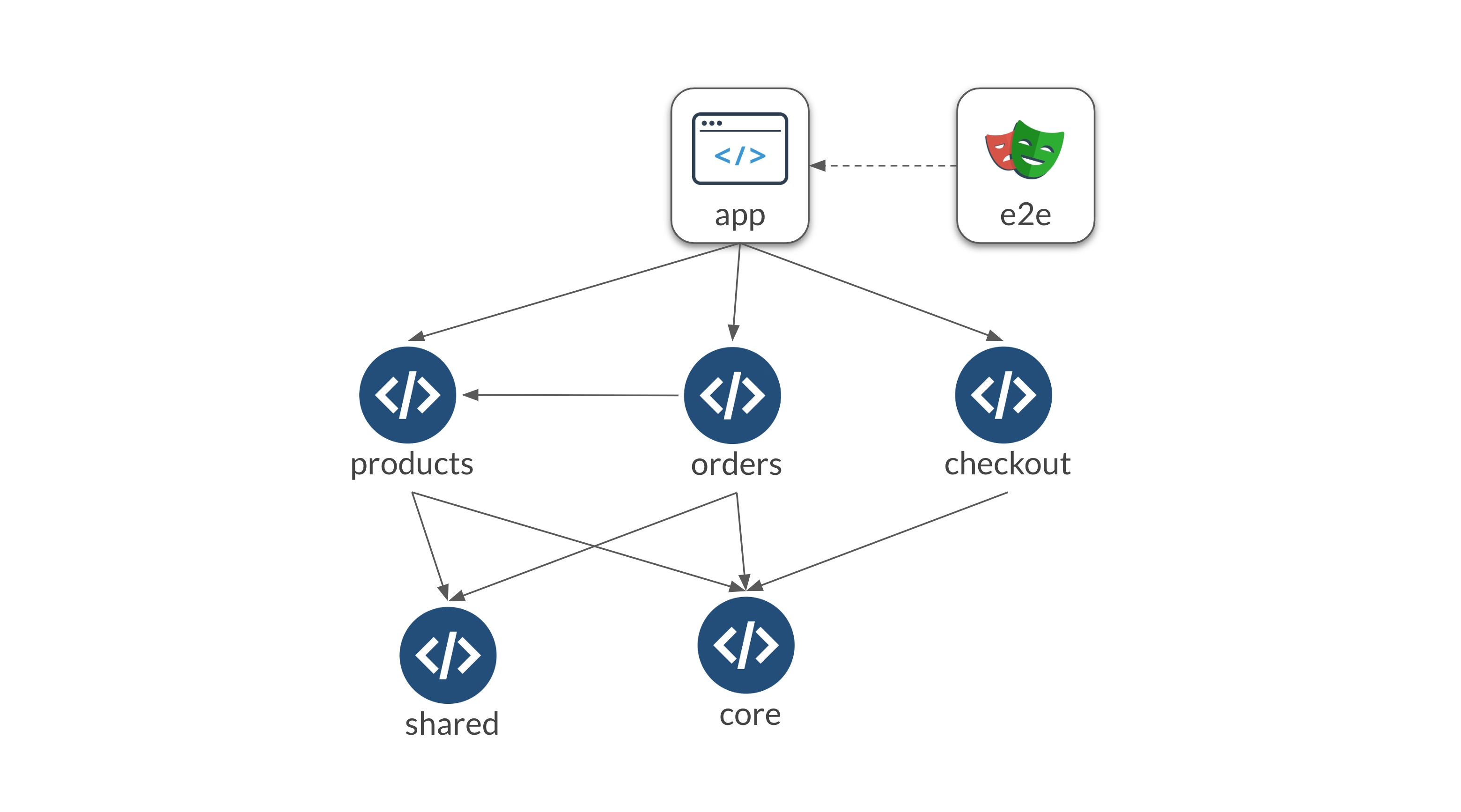
Our E2E project contains tests for each of the application features - products, orders and checkout. Any change made in the graph will cause all our E2E tests to be re-run. Even if we only modified products, we will still re-run the tests for orders and checkout. Although the Atomizer will help us split that work per file and distribute it, we will still end up running unnecessary work.
By defining scopes that implicitly depend on feature libraries rather than the entire application, you can ensure that only relevant tests are run when changes are made.
- Scope Definition: Break down your E2E tests into smaller, focused scopes.
- Dependency Management: Ensure that scopes depend on specific feature libraries, reducing unnecessary test execution.
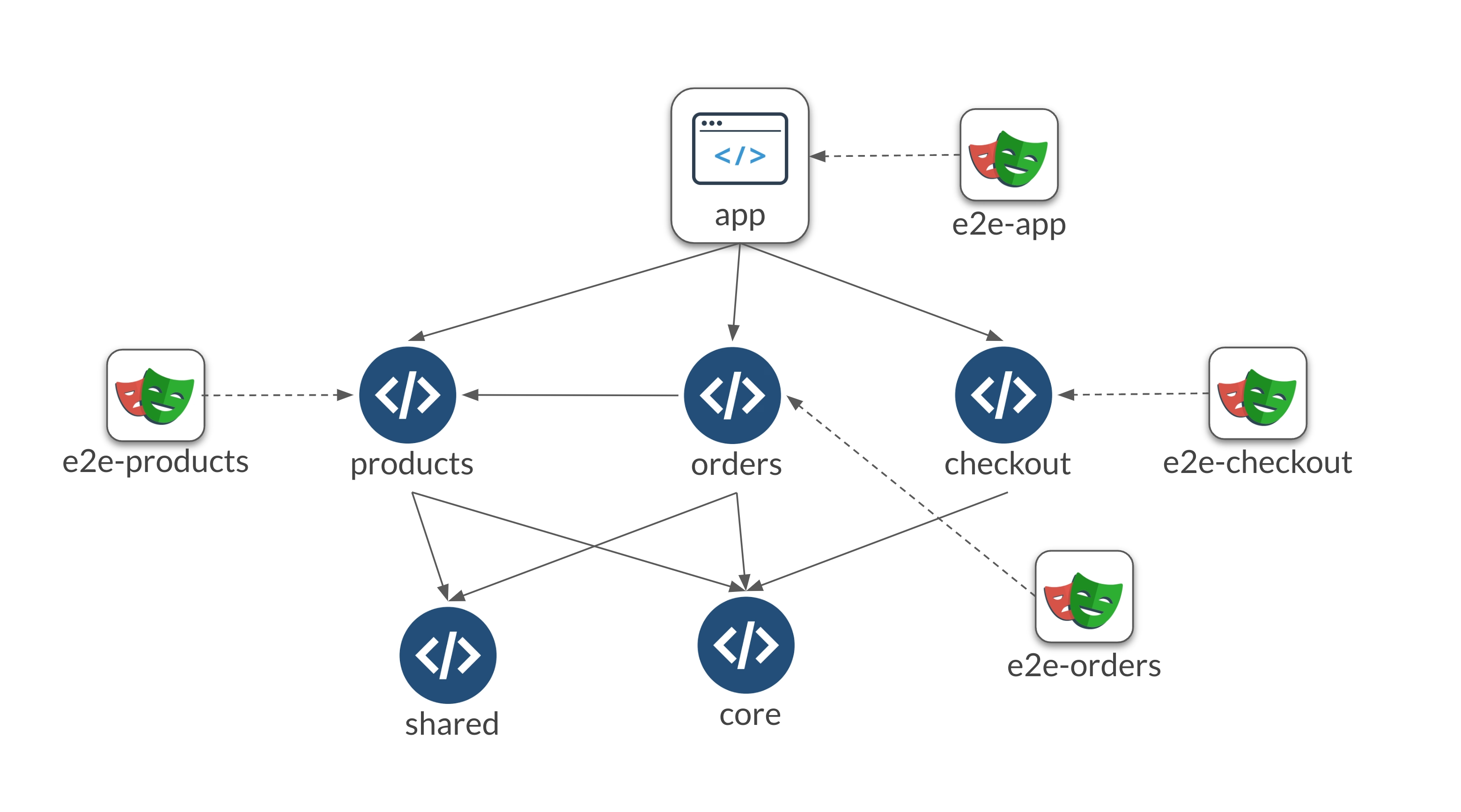
This approach offers both speed of distribution and caching efficiency. Every time the application is affected, we will only run the small subset of sanity smoke tests to ensure the application still runs, but specific features will only be tested if the relevant feature library has been modified or affected and skipped otherwise.
The tricky part comes from the fact that our split E2E applications still depend on the full application being served. But using the combination of implicitDependencies and dependsOn we can ensure that the application is running for our E2E tests without explicitly depending on it.
1{
2 ...
3 "implicitDependencies": ["checkout"],
4 "targets": {
5 "e2e": {
6 "dependsOn": ["^build", { "target": "build", "projects": "app" }]
7 }
8 }
9}
10When we look at the graph, we will only see an edge from checkout-e2e to checkout, but having an explicit dependsOn app:build ensures that the build of the application was successful and the distributed agent running our E2E task has app's build cache replayed.
As of Nx version 20.8.0 you can now combine manual splitting with the Atomizer. In order to split atomized projects, we will have to override their dependsOn property to target also app:build:
1{
2 ...
3 "implicitDependencies": ["checkout"],
4 "targets": {
5 "e2e": {
6 "dependsOn": ["^build", { "target": "build", "projects": "app" }]
7 },
8 "e2e-ci--**/**": {
9 "dependsOn": ["^build", { "target": "build", "projects": "app" }]
10 }
11 }
12}
13This small improvement gives us the best of both worlds - using the Atomizer to automatically split long running tasks into smaller chunks and using manual splitting to skip entire work if dependencies haven't changed.
Conclusion
By implementing these techniques — the built-in test sharding, Nx Atomizer, and manual E2E project splitting — you can significantly cut down CI time. That means fewer bottlenecks, less time waiting on pipelines, and more time spent delivering features, fixing bugs, and improving the product. When CI runs faster, teams can iterate quickly, merge with confidence, and ship value to users without the drag of slow test cycles.
Faster CI is just the beginning. When combined with Nx Cloud's distributed task execution, these strategies not only bring stability and improved performance but also offer better developer ergonomics and a comprehensive overview of your testing processes. This powerful combination allows your team to ship with greater confidence.
Give these techniques a try and see the difference for yourself.
Ready to go further?Let's talk about how Nx Cloud can help you scale with speed.





